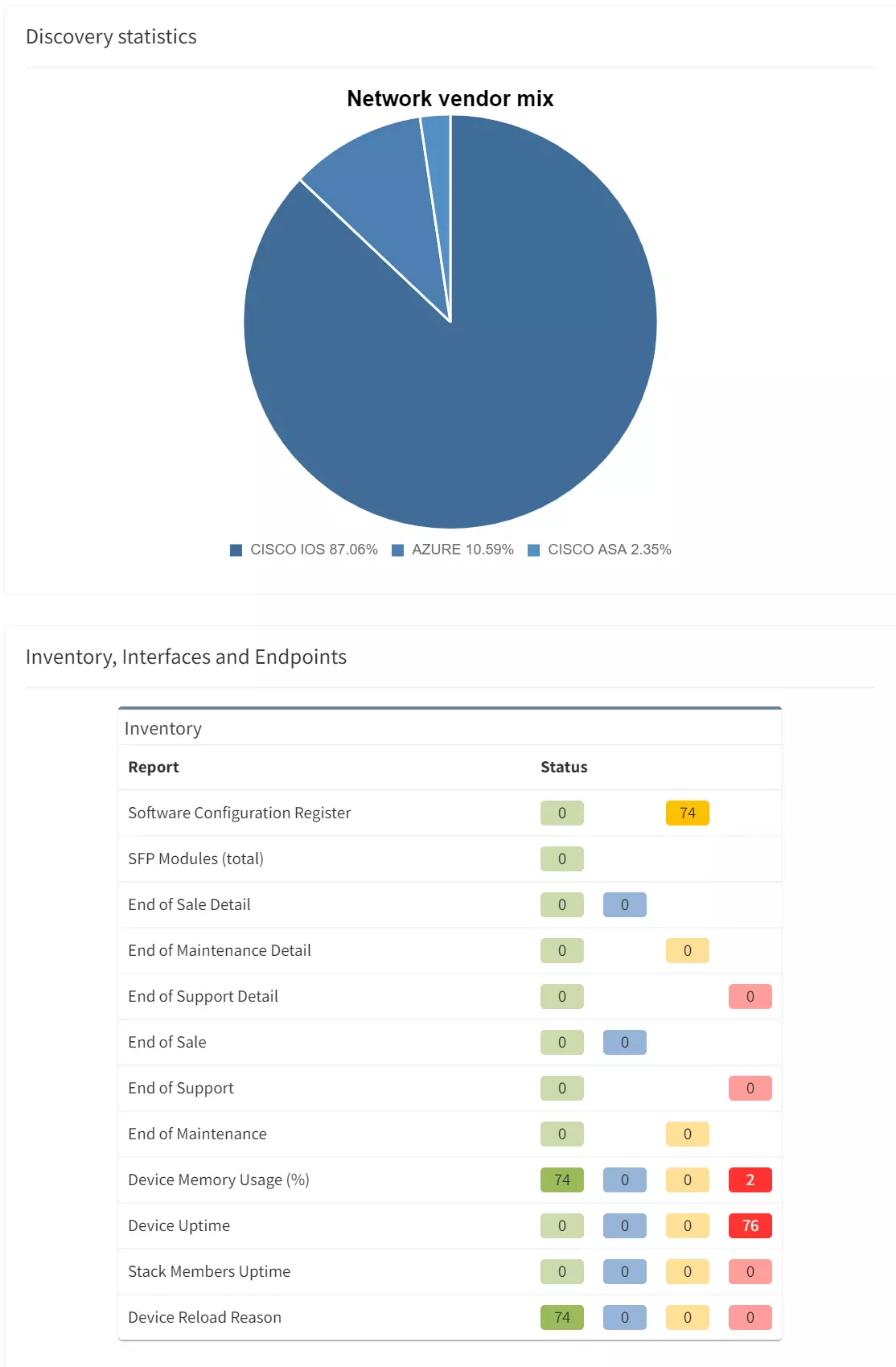
There should be minimal changes in the layer 2 switching operations — the switching topology should be constant and the number of MAC address moves minimally.
How do you know that the switching domain is not re-converging every minute or two due to STP issues?
Many problems in the current Ethernet layer 2 switched networks can come as a result of the behavior of the Spanning Tree Protocol and its derivatives. Its fail-open nature can render large parts of the network belonging to the same switching domain unusable. There are hints in STP operation before the major disruption happens which could be used as early warnings.
A number of topology changes, number of MAC address moves, STP diameter size, per VLAN root switch assignment, virtual port numbers and other operational values — if those will find a way to network engineer, they can mitigate the issue before the switching domain goes down completely. However, it is not exactly easy to routinely gather and process detailed Spanning Tree Protocol outputs to see if something out of ordinary is starting to happen.
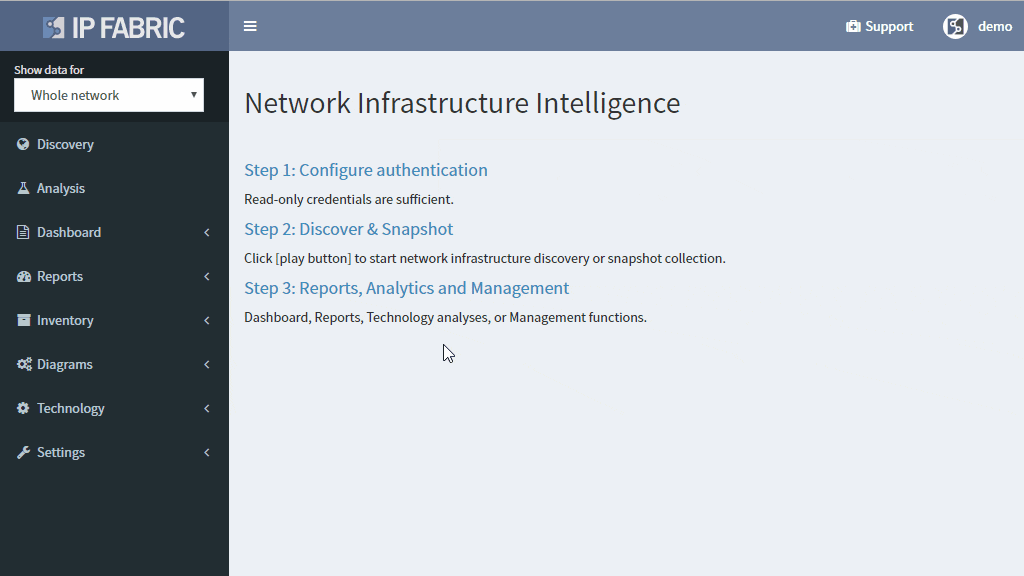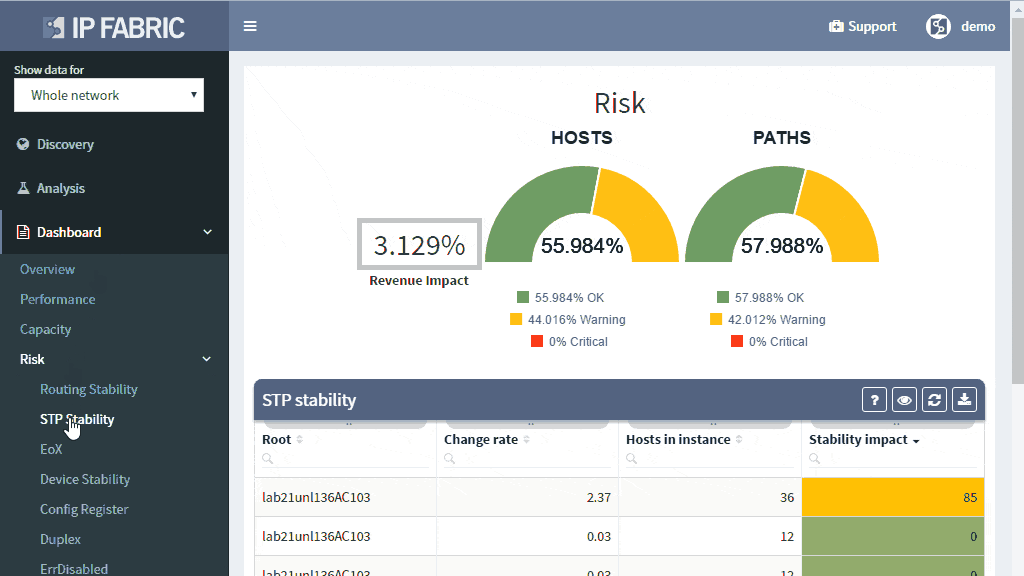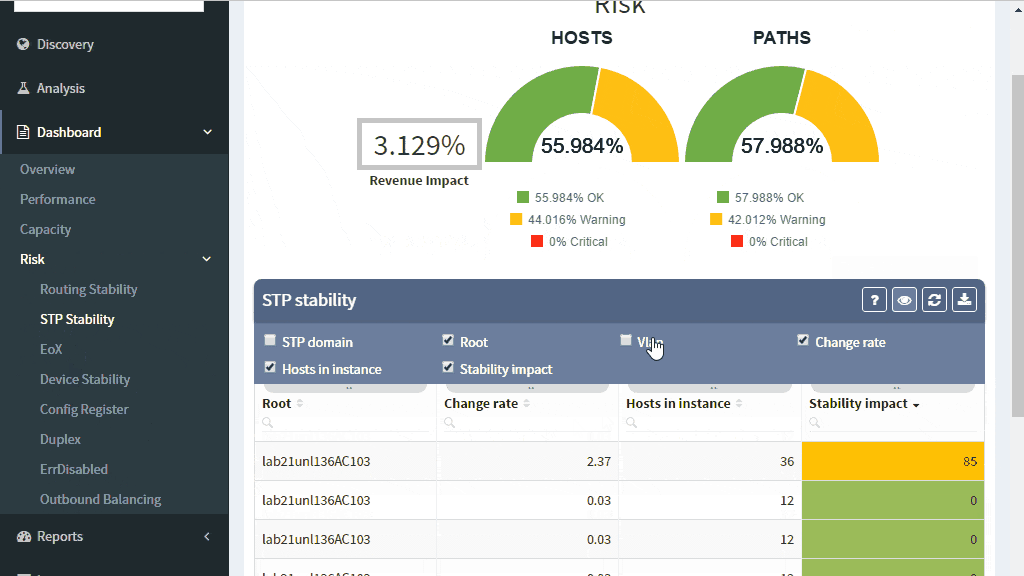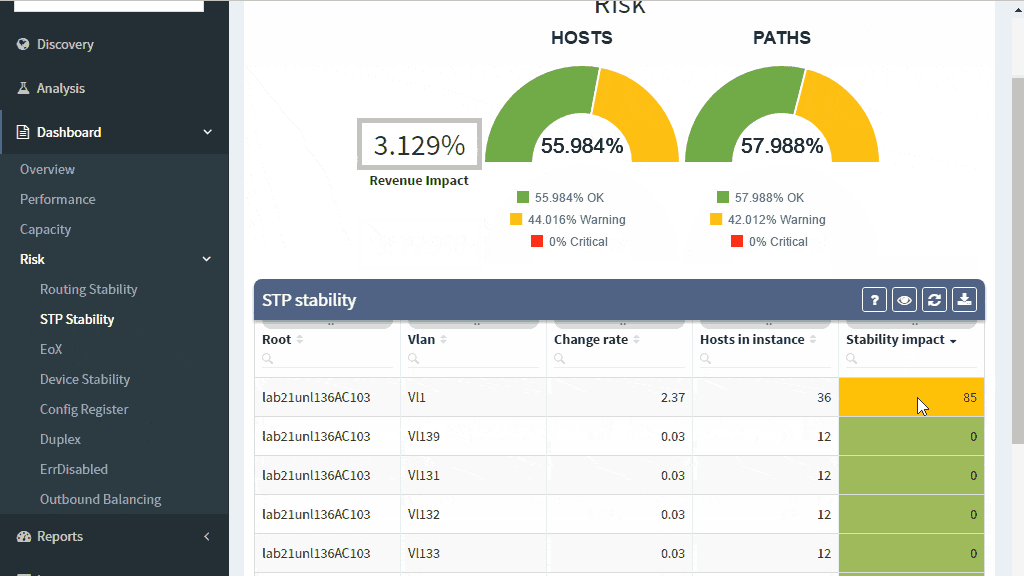
The IP Fabric platform collects STP data and processes those into various statistics which provide immediate guidance to network engineers, such as that the network is re-converging too frequently, or that the root bridge uses default priority value, or that the STP topology includes more switches than recommended by best practices.
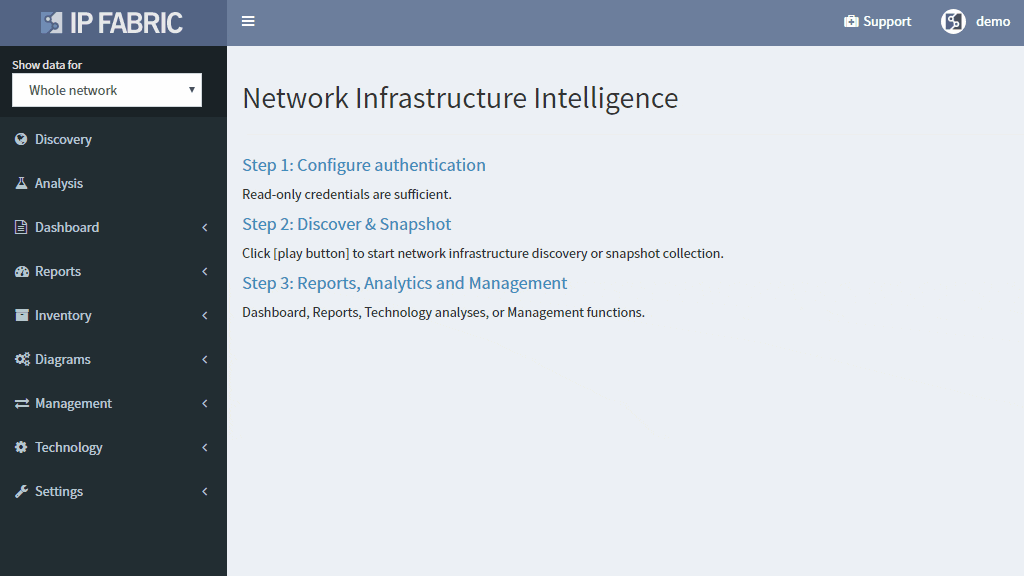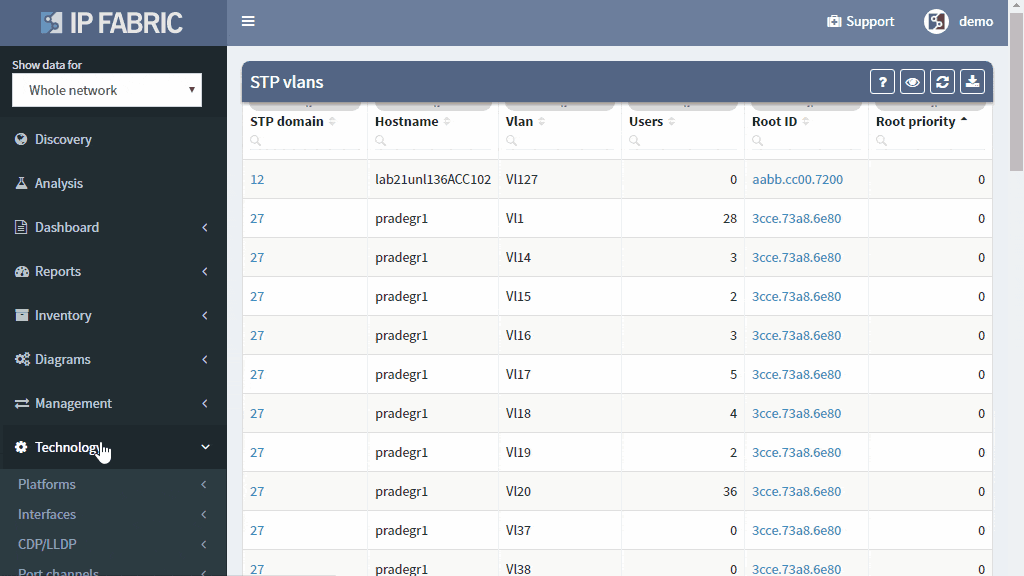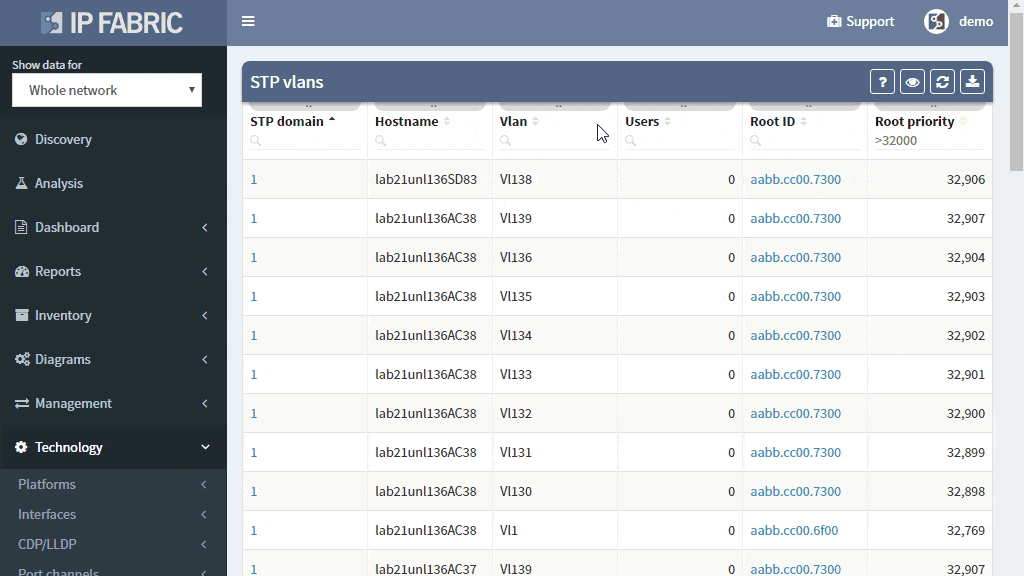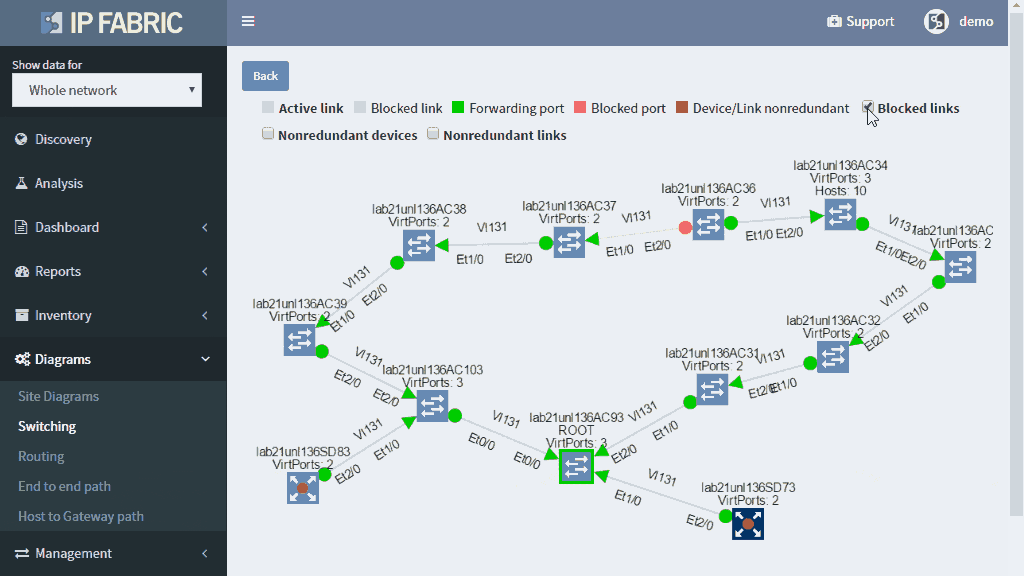
Detailed Spanning Tree analytics in the IP Fabric platform help engineers to investigate what could be wrong with the L2 switching domain, what could be fixed or changed, and help with the change procedure, such as switching to a newer derivative of the Spanning Tree protocol.
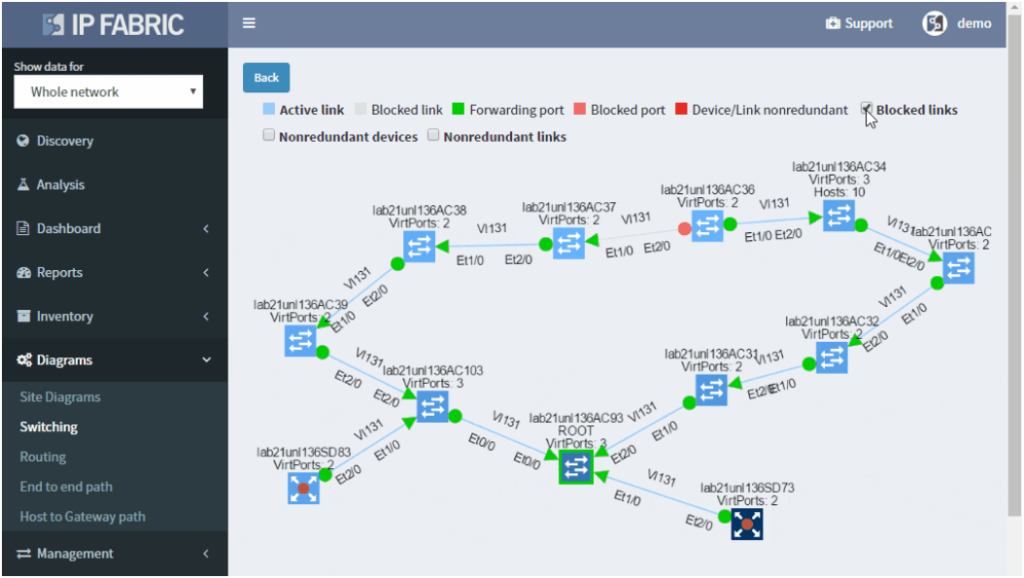
If you’re interested to see how the IP Fabric platform can help you to keep L2 switching domain stable, contact us for an online demo or a trial in your network. Also, we’re hiring!
There should be minimal changes in the layer 2 switching operations — the switching topology should be constant and the number of MAC address moves minimally.
How do you know that the switching domain is not re-converging every minute or two due to STP issues?
Many problems in the current Ethernet layer 2 switched networks can come as a result of the behavior of the Spanning Tree Protocol and its derivatives. Its fail-open nature can render large parts of the network belonging to the same switching domain unusable. There are hints in STP operation before the major disruption happens which could be used as early warnings.
A number of topology changes, number of MAC address moves, STP diameter size, per VLAN root switch assignment, virtual port numbers and other operational values — if those will find a way to network engineer, they can mitigate the issue before the switching domain goes down completely. However, it is not exactly easy to routinely gather and process detailed Spanning Tree Protocol outputs to see if something out of ordinary is starting to happen.

The IP Fabric platform collects STP data and processes those into various statistics which provide immediate guidance to network engineers, such as that the network is re-converging too frequently, or that the root bridge uses default priority value, or that the STP topology includes more switches than recommended by best practices.

Detailed Spanning Tree analytics in the IP Fabric platform help engineers to investigate what could be wrong with the L2 switching domain, what could be fixed or changed, and help with the change procedure, such as switching to a newer derivative of the Spanning Tree protocol.

If you’re interested to see how the IP Fabric platform can help you to keep L2 switching domain stable, contact us for an online demo or a trial in your network. Also, we’re hiring!